Thompson Sampling in Bernoulli Bandits
In this post, I will implement Thompson Sampling in a Bernouli bandit problem in Python and compare it with the performance of the greedy algorithm. This page is simply implementing the algorithms elegantly explained in this paper.
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltThis is the implementation of the greedy algorithm in the paper
def greedy_update_posterior_params(T, rewards):
beta = [1 for _ in rewards]
alpha = [1 for _ in rewards]
bins = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
for t in range(1,T+1):
theta = []
for k in range(len(rewards)):
theta.append(alpha[k]/(alpha[k]+beta[k]))
max_idx = max(range(len(rewards)), key=lambda i:theta[i])
r = rewards[max_idx]
beta[max_idx] += 1-r
alpha[max_idx] += r
if t % 100 == 0:
plt.figure(figsize=(14,4))
for j in range(len(rewards)):
armj = [np.random.beta(alpha[j], beta[j]) for _ in range(1000)]
plt.hist(armj, bins, alpha=0.5, label='arm {}'.format(j))
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()
return alpha, betaHere is also the implementation of the Thompson Sampling algorithm for the Bernoulli bandit with Beta prior distribtuion.
def thompson_sampling_update_posterior_params(T, rewards):
beta = [1 for _ in rewards]
alpha = [1 for _ in rewards]
bins = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
for t in range(1,T+1):
theta = np.random.beta(alpha, beta).tolist()
max_idx = max(range(len(rewards)), key=lambda i:theta[i])
r = rewards[max_idx]
beta[max_idx] += 1-r
alpha[max_idx] += r
if t % 100 == 0:
plt.figure(figsize=(14,4))
for j in range(len(rewards)):
armj = [np.random.beta(alpha[j], beta[j]) for _ in range(1000)]
plt.hist(armj, bins, alpha=0.5, label='arm {}'.format(j))
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()
return alpha, betaHere is the result of running these algorithms
alpha, beta = greedy_update_posterior_params(500, [0.1,0.8,0.6,0.3])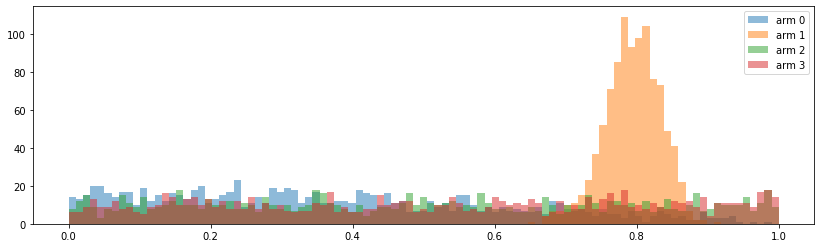
alpha, beta = thompson_sampling_update_posterior_params(500, [0.1,0.8,0.6,0.3])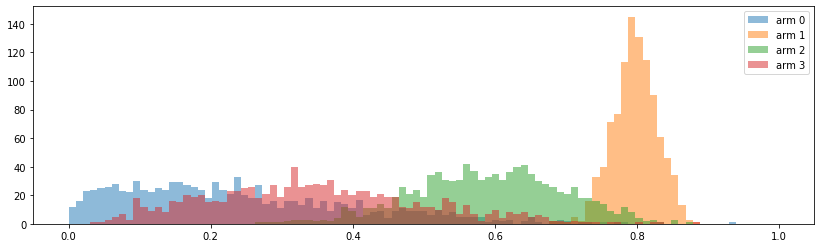 A summary of this code is available in this notebook.
A summary of this code is available in this notebook.